Table of Contents
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder, which can be characterized by difficulties in communication, social interactions, and repetitive behaviors. The term spectrum refers to the wide range of symptoms, skills, and levels of impairment that people with ASD may experience.
The exact cause of ASD remains unknown, although research suggests that both genetics and environmental factors play a role. It is generally accepted that ASD begins before a child is three years old. However, the signs and symptoms of ASD vary greatly among affected individuals.
There is no single medical test to diagnose ASD; instead doctors evaluate a person’s behavior and development using standard diagnostic procedures. These procedures may include assessments by a team of health care professionals, including psychologists, psychiatrists, pediatricians, and other specialists. The team also may include family members or guardians who have observed the child over time and can provide information about the child’s behaviors and development.

What Are The Three Main Characteristics or Symptoms of Autism?
Autism is a developmental disorder that manifests in early childhood and lasts throughout an individual’s lifetime. It affects 1 in 68 children, typically at the age of 3 or 4, making it the most prevalent developmental disorder in the United States. Autism is defined by three main characteristics:
- Impaired social interaction
- Dysfunctional verbal and nonverbal communication
- Rigid and repetitive patterns of behavior
The first characteristic is that autism impairs social interaction. People with autism have difficulty understanding what other people are thinking and feeling, or empathizing with others. This can make them appear aloof or insensitive, when in fact they’re just struggling to understand the motivations behind what someone says or does. They also may struggle to make friends, since they have trouble understanding how to interact socially.
Examples of autistic social impairment include: not being able to direct attention to things most people would notice (for example, being oblivious to changes in facial expression), taking words literally rather than figuratively, not knowing how to start or maintain a conversation, and having difficulty interpreting tone of voice or facial expressions such as smiling. Autistic people might also lack nonverbal communication skills like eye contact and facial expressions, or they might be unable to read body language in others.
What Are The 3 Types of Autism?
Autism is defined as a spectrum of disorders that share several symptoms. These include repetitive behaviors, difficulties with social interactions and challenges with communication. These symptoms vary in severity from one individual to another, which is why it’s important to understand the three classifications of autism.
The three classifications of autism are:
Autism disorder (ASD) – People with this diagnosis often have significant difficulties in social interaction and verbal and nonverbal communication, as well as restricted interests and repetitive behaviors. These individuals may also engage in self-injurious behavior or have extreme difficulty adapting to changes in their environment. This is the most severe classification of autism spectrum disorder.
Asperger syndrome (AS) – The primary characteristics of AS are significant difficulties in social interaction and verbal and nonverbal communication, along with restricted, repetitive or stereotyped patterns of behavior. However, unlike those who have ASD, people with AS are not significantly impaired by their symptoms, nor do they need services provided specifically for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Pervasive developmental disorder – Not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS) – People with this diagnosis generally display the same characteristics as individuals diagnosed with ASD; however, their symptoms do not meet the specific criteria for ASD.
How Are Autism and ADHD Related?
Autism and ADHD are two distinct conditions with different symptoms, causes, and treatments. Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder that includes impairments in social interaction and communication skills, along with repetitive behaviors or restricted interests. ADHD is a neurobehavioral condition marked by hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention.
When children have both autism and ADHD, it doesn’t matter which came first — their needs require separate treatment approaches to maximize their potential for success and happiness. However, there are several overlapping issues to consider when planning for your child’s future day-to-day life:
Treatment for one condition does not necessarily mean the other condition will improve as well. Children with autism should be evaluated for ADHD because symptoms commonly co-exist, but stimulant medication does not treat core symptoms of autism like deficits in social skills or communication. Stimulants can help improve attention span and decrease hyperactivity in children with both conditions but may worsen repetitive behaviors or other autistic symptoms.
What Causes Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
The cause of autism is not known at present. It is believed to be caused by abnormalities in brain structure or function. Brain scans show differences in the shape and structure of the brain in children with autism compared to in neurotypical children. Researchers do not know the causes of these differences yet.
There is no doubt that genes are involved, as ASD tends to occur more often in families, especially when there are two or more boys in the family. But ASD can also occur in families with no history of autism.
Genetic or genetic and environmental factors are the likely causes of ASD. Genetic factors alone may account for 50% of ASD cases, while other cases may be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
The following factors have been associated with increased risk for ASD:
- Advanced parental age at the time of conception (both mom and dad)
- Being born prematurely (before 35 weeks gestation)
- Having a sibling with ASD
Other non-genetic risks include:
- Certain infections during pregnancy, such as rubella (German measles)
- Valproic acid (an anti-seizure medication) or thalidomide (used to treat certain cancers and skin conditions) taken by the mother during pregnancy
- Exposure to pollutants such as pesticides, air pollutants, mercury, PCBs, and dioxins in the environment
How and When Is Autism Diagnosed?
The average age for diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the United States is about 5 years of age. It’s not unusual for a child to be diagnosed by age 3 or 4, but it also can take longer. In some cases, an early diagnosis can be made in children as young as 2 years old.
Some parents and health professionals are concerned that many children with ASD are not being diagnosed until school age or even later. This can happen for a number of reasons:
- Lack of awareness about autism symptoms and behaviors
- Misdiagnosis of other conditions (such as developmental delays)
- Delays in getting evaluation services
- Delays in getting appropriate treatment services

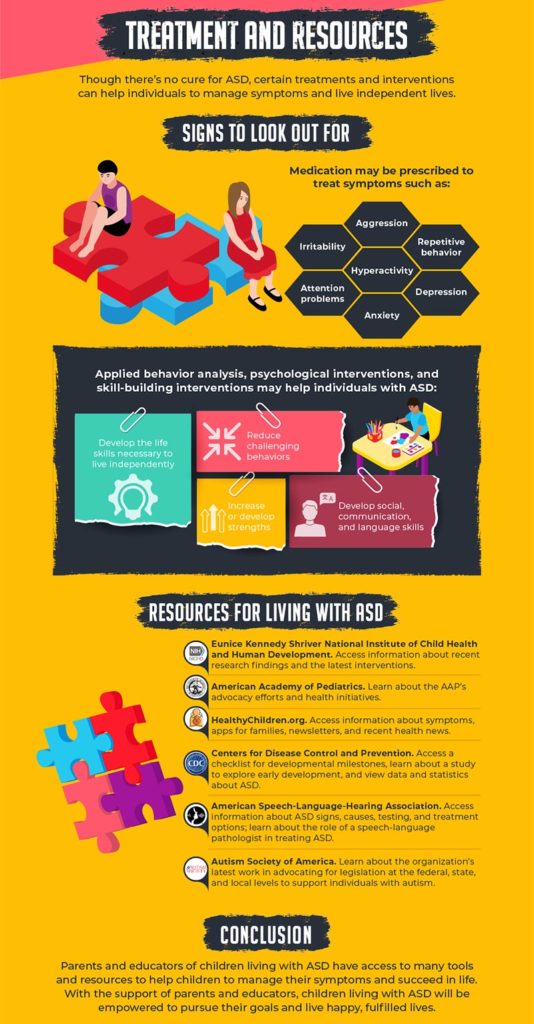
What Are the Treatment Options for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
There are many treatment options available for ASD. Early intervention is critical, and a specialist can help decide which treatments are most appropriate for the individual.
Early intervention services include:
- Speech-language therapy to help with communication skills
- Occupational therapy to improve daily living skills and motor coordination
- Physical therapy to work on strength and coordination
- Applied behavioral analysis (ABA) to break down skills needed into small steps, then teach them individually
Autism Spectrum Disorder At a Glance
ASD is diagnosed four times more often in boys than girls. The prevalence of ASD has increased over the last two decades. About 1 in 59 children have been identified with ASD, according to estimates from CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network.
ASD occurs in all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups but is roughly 30% more common among boys than girls.
There is no known single cause for autism spectrum disorder, but it is generally accepted that it is caused by abnormalities in brain structure or function. Brain scans show differences in the shape and structure of the brain in children with autism compared to in neurotypical children.
Researchers don’t know the exact cause of autism but are investigating a number of theories, including the links among heredity, genetics and medical problems. In many families, there appears to be a pattern of autism or related disabilities, further supporting the theory that the disorder has a genetic basis.
Autism Clinical Trials
Autism clinical trials are research studies done with people to look at new ways of diagnosing, preventing, or treating disease. Clinical trials are designed to answer questions about new therapies, medications, or procedures that may improve the health of people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Medical devices and tests. Researchers also use clinical trials to test new medical devices and procedures. Clinical trials that study devices will test how well the devices work and whether they are safe for people with autism.
Who can participate in a clinical trial?
Clinical trials may have specific guidelines about who can participate. Before joining a clinical trial, a person must qualify for the study. Some research studies seek volunteers with illnesses or conditions to be studied in the clinical trial, while others need healthy participants. There are usually requirements regarding age and other medical conditions. It is important to note that inclusion and exclusion criteria vary from study to study.
How is a clinical trial planned?
Each clinical trial has a protocol, or action plan, for conducting the trial. The plan describes what will be done during the study, how many people will take part in it, and what kinds of tests and procedures will be done during the trial.